Oldest Countries in the World: San Marino & Sovereign States
Explore the oldest countries in the world, from San Marino to Iran. Discover ancient civilization, sovereignty, and identifying the oldest nations.

Exploring the concept of the oldest countries in the world involves navigating a complex interplay of history, sovereignty, and civilization. Defining what constitutes one of the oldest independent countries requires careful consideration of its founding date, early history, and continuous existence as a sovereign state. Examining these countries offers insights into the rise and fall of empires and the enduring spirit of nations.
Importance of Historical Context
Understanding the historical context is crucial when identifying the oldest countries in the world. The age of a country is not merely a matter of dates; it reflects a continuous thread of cultural, political, and societal development. For example, certain countries date back thousands of years, with their early history intertwined with ancient civilizations and their lasting impact on the world stage. Historical narratives are essential to understanding the complexities of national identity and sovereignty.
Criteria for Classification as Oldest
Several criteria are used to classify the oldest nations in the world. Verifiable founding date, Continuous sovereigntyAnd also the extent to which the country's current form reflects its early history. A country's ability to have remained independent throughout centuries of conquest and shifting geopolitical landscapes plays a crucial role. These criteria help to differentiate between entities with ancient roots and modern sovereign states.
Exploring Other Oldest Countries
1. San Marino

San Marino, often cited as one of the oldest countries, traces its origins back to 301 AD. It lays claim to being the oldest republic and one of the oldest continuous sovereign states in the world. While its size is diminutive, San Marino has remarkably maintained its sovereignty through centuries, avoiding conquest and involvement in larger empires, thus solidifying its place among the oldest nations.
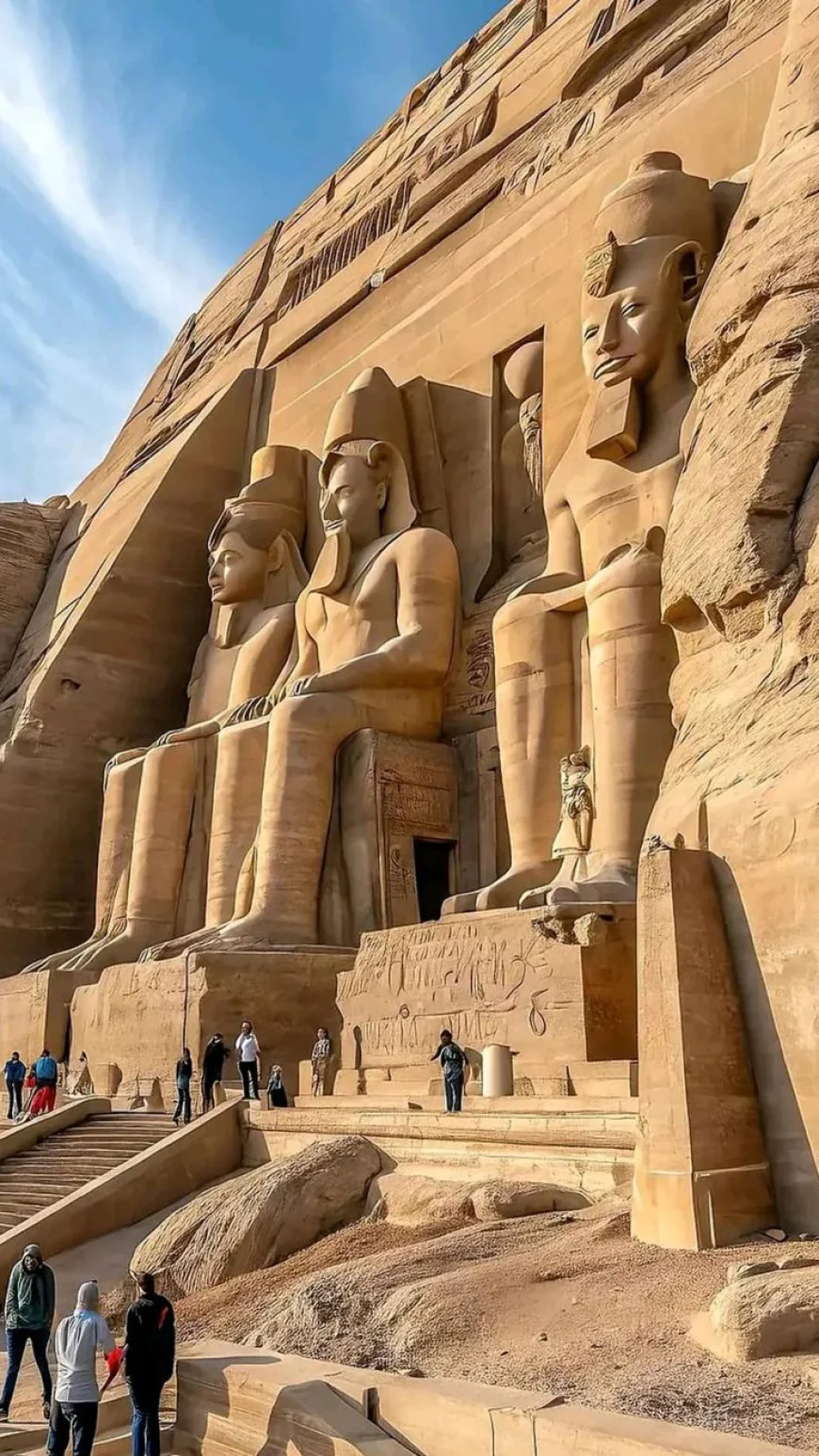
2. Egypt

Ancient Egypt, specifically Lower Egypt, boasts a history that dates back thousands of years, with its early history closely tied to the oldest civilizations. The unification of Upper and Lower Egypt marks a pivotal moment. Egypt’s ability to maintain a distinct cultural identity while often being influenced by various empires underscores its enduring significance as one of the oldest countries in the world.
3. China

China’s history is characterized by successive dynasties and empires, such as the Shang Dynasty, each contributing to the country’s evolving identity. Despite periods of fragmentation and conquest, the idea of a unified China has persisted for thousands of years. The Republic of China faces complex issues. This continuity places China among the oldest nations in the world, reflecting the enduring impact of ancient civilization.
4. Japan

With a founding date traditionally placed around 660 BC, Japan is one of the oldest nations. Japan has evolved from an ancient kingdom into a modern sovereign state while preserving unique cultural traditions. Throughout its history, Japan has experienced periods of isolation and engagement with the outside world, shaping its identity and solidifying its status among the oldest countries.
5. Greece

Greece, particularly Athens, holds a prominent position as the cradle of Western civilization. Its city-state system and philosophical advancements laid the groundwork for modern political thought. Despite periods of conquest by various empires, Greece has maintained a strong sense of cultural identity. Greece gained independence. Its historical significance places Greece among the oldest countries.
6. Ethiopia

Ethiopia stands out as one of the oldest countries in Africa, with a history dating back thousands of years. Unlike many other African nations, Ethiopia was not colonized during the Scramble for Africa and remained independent. This unique status has allowed Ethiopia to preserve its cultural and political heritage, solidifying its place among the oldest nations in the world.
7. Armenia

Armenia is considered one of the oldest countries in the Caucasus region, with a rich history that dates back to antiquity. It was the first state to adopt Christianity as its state religion in the early 4th century. This early adoption of Christianity has profoundly influenced Armenian culture and identity. It has allowed Armenia to solidify its place among the oldest nations.
8. India

The Indian subcontinent is home to one of the oldest civilizations, the Indus Valley Civilization, which flourished thousands of years ago. Ancient kingdoms and empires have shaped the region’s history. India’s ability to maintain a distinct cultural identity through centuries of conquest and shifting geopolitical landscapes underscores its enduring significance as one of the oldest countries in the world.
9. Iran

Iran, formerly known as Persia, boasts a rich history dating back to the Achaemenid Empire. Its cultural and political influence has extended throughout the Middle East and beyond. Iran maintained its cultural identity while often being influenced by various empires. The country’s contributions to art, science, and philosophy highlight its enduring significance as one of the oldest nations.
10. Portugal

Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is one of the oldest nations in Europe. Portugal's early history is a story of strategic alliances, maritime exploration, and the establishment of a vast colonial empire. Its maritime power and influence in global trade contributed to its cultural and economic development, securing its position among the oldest countries in Europe.
11. France

France, with its roots stretching back to ancient Gaul and the Frankish kingdom, boasts a rich tapestry of history. The medieval Kingdom of France evolved into a major European power, marked by the reign of influential dynasties and pivotal events like the French Revolution. France's cultural contributions, from art and literature to philosophy and fashion, have shaped Western civilization, affirming its status among the oldest nations.
12. Turkey

Turkey's historical narrative is deeply intertwined with the rise and fall of empires. Anatolia, the heartland of modern-day Turkey, served as a bridge between Europe and Asia. Turkey's location has made it a crossroads of cultures and empires, contributing to its unique identity and positioning it among the oldest countries with a rich and diverse heritage.
13. Israel

Israel's history is deeply rooted in ancient traditions and religious significance. The land of Israel holds a central place in Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Despite periods of dispersion and foreign rule, the Jewish people maintained a connection to their ancestral homeland. Israel’s modern state formation represents a renewal of ancient identity and sovereignty.
14. Nepal

Nepal, nestled in the Himalayas, boasts a history steeped in ancient traditions and cultural diversity. The kingdom's isolation fostered a unique blend of indigenous beliefs and practices. Nepal's ability to safeguard its independence amid geopolitical shifts contributed to its distinctive identity and solidified its status among the oldest countries. Nepal wasn't colonized by the British empire.
15. Georgia

Georgia, strategically located at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, possesses a rich history marked by cultural exchange and resilience. From ancient kingdoms to medieval principalities, Georgia's narrative is one of constant struggle for sovereignty. Despite facing numerous invasions and foreign domination, Georgia maintained its distinct cultural identity, solidifying its place among the oldest nations.
16. Vietnam

Vietnam, steeped in ancient history and cultural heritage, has emerged as a vibrant nation in Southeast Asia. From the Bronze Age Dong Son culture to the rise of powerful kingdoms and dynasties, Vietnam's narrative is one of continuous evolution. Vietnam's journey through periods of colonization, war, and reunification has shaped its identity. The country has solidified its position among the oldest countries.
17. Korea

Korea, nestled on the Korean Peninsula, boasts a history marked by ancient kingdoms, cultural innovation, and resilience. From the founding of Gojoseon to the rise of powerful dynasties like Silla and Goryeo, Korea's narrative is one of continuous cultural development. Korea has preserved its unique identity amid geopolitical challenges. The state has secured its place among the oldest countries.
18. Mongolia

Mongolia, with its vast steppes and nomadic traditions, boasts a history shaped by empires and cultural exchange. From the rise of the Mongol Empire under Genghis Khan to the establishment of modern Mongolia, the country's narrative is one of resilience and adaptability. Despite periods of foreign domination, Mongolia maintained its distinct cultural identity, earning its place among the oldest nations.
19. Iraq

Iraq, cradled in the fertile lands of Mesopotamia, holds a distinguished place in the annals of human civilization. As the birthplace of some of the oldest civilizations, including the Sumerians, Babylonians, and Assyrians, Iraq's narrative is intertwined with innovation and intellectual achievements. Iraq has earned its place among the oldest countries with a rich and diverse heritage.
20. Afghanistan

Afghanistan, situated at the crossroads of Central and South Asia, boasts a history characterized by empires, conquests, and cultural exchange. From the ancient Persian empires to the rise of Islamic dynasties, Afghanistan's narrative is one of resilience and adaptation. Despite facing numerous invasions and periods of instability, Afghanistan has maintained its distinct cultural identity, earning its place among the oldest countries.
21. Spain

Spain's historical narrative is a tapestry woven with threads of ancient civilizations, Roman conquest, and the rise of a powerful empire. From the Iberian tribes to the arrival of the Visigoths and the subsequent Moorish rule, Spain's territory witnessed a confluence of cultures and influences. Its status as one of the oldest continuous countries with a rich and diverse heritage.
22. United Kingdom

The United Kingdom, an island nation with a global legacy, boasts a history shaped by conquest, exploration, and empire-building. From the Roman invasion of Britain to the rise of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms and the Norman Conquest, the British Isles witnessed a succession of transformative events. The United Kingdom gained independence and solidified its position among the oldest nations.
23. Morocco

Morocco, strategically located at the crossroads of Africa and Europe, boasts a history marked by ancient civilizations, Islamic dynasties, and cultural exchange. From the Berber kingdoms to the Almoravid and Almohad empires, Morocco's narrative is one of resilience. Morocco’s historical significance places the country among the oldest countries, showcasing a diverse heritage.
24. Bulgaria

Bulgaria, nestled in the heart of the Balkans, boasts a history that intertwines ancient civilizations, medieval kingdoms, and cultural renaissance. From the Thracians and Romans to the rise of the First and Second Bulgarian Empires, Bulgaria's narrative is one of cultural synthesis. Bulgaria's enduring contributions to literature, art, and architecture highlight its significance as one of the oldest nations in Europe.
25. Denmark

Denmark, with its roots tracing back to the Viking Age, is one of the oldest countries in Scandinavia and Europe. From the unification of the Danish kingdom to its influence in the medieval Kalmar Union, Denmark's history is marked by maritime power and cultural exchange. Denmark has remained independent and solidified its position among the oldest nations in the world.
San Marino: A Unique Sovereign State
San Marino, laying claim to being one of the oldest countries in the world, traces its founding date back to 301 AD. According to tradition, the nation was founded by Saint Marinus, a Christian stonemason, on Mount Titano. This early history distinguishes San Marino as the oldest continuous republic and one of the oldest extant sovereign states globally. The ideals of freedom and self-governance have been central to San Marino's identity since its inception.
Conclusion: Legacy of the Oldest Countries
The impact of the oldest countries on global civilization is immeasurable. These nations, some dating back thousands of years, have shaped political systems, cultural norms, and technological advancements. Their early history, intertwined with the rise and fall of empires and kingdoms, offers invaluable lessons. By studying these oldest nations in the world, we gain a deeper understanding of human resilience and the enduring quest for sovereignty.
FAQS
Q1: Which is the oldest country in the world?
Identifying the oldest countries is challenging because the definition of a country depends on various factors such as continuous sovereignty and founding date. However, San Marino, founded in 301 AD, is often cited as one of the oldest continuous republics. Other contenders include countries with ancient roots such as Iran, Ancient Egypt, and Armenia, each boasting histories spanning thousands of years.
Q2: Is there a country older than Egypt?
Ancient Egypt, particularly Lower Egypt, is among the oldest civilizations with a history that dates back to the predynastic period. Several other countries, such as Iran and Armenia, also lay claim to ancient origins. While Egypt's civilization flourished millennia ago, whether it is definitively the "oldest" depends on specific criteria like continuous governance and cultural identity.
Q3: How oldest country in the world
Determining the oldest country in the world depends on defining "country." If we consider sovereignty and continuous existence, San Marino, established in 301 AD, often tops the list. However, if we focus on the age of a country based on civilization origins, nations like Iran, ancient Egypt, or those within the Indian subcontinent, might be considered one of the oldest due to their rich, ancient pasts.
Q4: When was the first civilization in the world
The earliest known civilizations emerged in Mesopotamia and the Nile Valley several thousands of years ago. The Sumerian civilization in Mesopotamia, dates back to around 4500 BC, while the civilization of Ancient Egypt, particularly in Lower Egypt, arose around 3100 BC. The Indus Valley civilization on the Indian Subcontinent also flourished around 3300 BC, marking these as some of humanity's earliest urban societies.
Q5: Why is egypt the oldest country in the world
While Egypt is undeniably among the oldest countries in the world, pinpointing it as definitively the "oldest" depends on the criteria. Ancient Egypt, including Lower Egypt, boasts a history that dates back thousands of years. The question of whether Egypt is the "oldest" often depends on how one defines "country"—whether by continuous sovereignty, cultural identity, or the existence of early civilizations.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0